When you think of Sarcosuchus, or "SuperCroc," envision a giant prehistoric crocodile that could reach lengths of up to 12 meters (40 feet) and weigh about 8 metric tons. This formidable predator thrived in tropical freshwater habitats during the Cretaceous period. With a massive skull and powerful jaws, it specialized in capturing fish and turtles. Its unique physical adaptations, like tough armor and a robust body, helped it dominate aquatic ecosystems. If you find this fascinating, there's so much more to discover about its history, habitat, and the incredible role it played in prehistoric life.
Key Takeaways
- Sarcosuchus, also known as "SuperCroc," could grow up to 12 meters (40 feet) long and weigh around 8 metric tons.
- It lived in lush, tropical freshwater environments during the Early Cretaceous period, thriving alongside large fish and turtles.
- Sarcosuchus had a unique skull structure with a long snout and powerful jaws, designed for capturing slippery prey.
- Fossils of Sarcosuchus have been found across Africa and Brazil, indicating a wide distribution in prehistoric ecosystems.
- Its adaptations and size made Sarcosuchus one of the largest and most effective predators of its time, surpassing modern crocodiles.
Description and Physical Characteristics

When you think of prehistoric predators, Sarcosuchus, commonly known as "SuperCroc," stands out with its impressive size and formidable features. This giant crocodile could reach lengths of up to 12 meters (40 feet) and weigh around 8 metric tons (8.8 short tons), making it one of the largest crocodyliforms to roam the Earth.
Its most striking physical characteristics include a unique skull structure, with the largest known specimen measuring about 1.6 meters (5.25 feet) long. The skull featured telescoped eyes and a long snout that comprised 75% of its overall length, enhancing its hunting capabilities. Top 5 Projectors for Gaming Enthusiasts in modern technology highlight the importance of specialized adaptations, much like those of Sarcosuchus.
Sarcosuchus boasted a powerful jaw, with 35 teeth per side on the upper jaw and 31 on the lower, perfectly adapted for grabbing and holding onto prey. Its robust body and strong jaws allowed it to exert immense pressure, reinforcing its status as a top predator in its ecosystem.
Additionally, recent research indicates that Sarcosuchus had adaptations for a semi-aquatic lifestyle, thriving in freshwater habitats during the Cretaceous period. These physical characteristics highlight the incredible prowess of Sarcosuchus as a dominant force in its prehistoric world.
Classification and Discovery
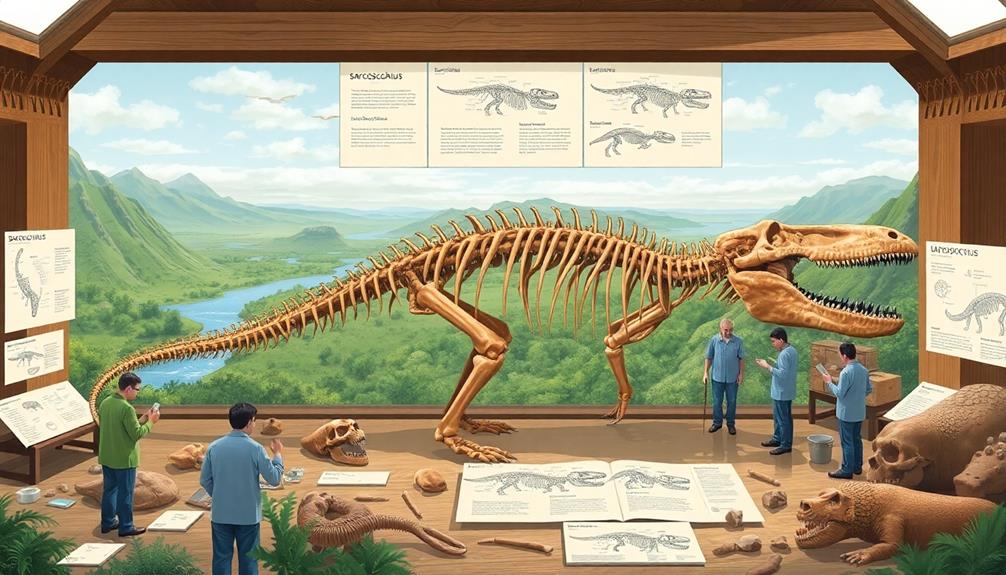
Let's explore how Sarcosuchus fits into the broader classification of crocodilians and its fascinating fossil discovery timeline.
You'll find that key researchers have played a significant role in uncovering its secrets, from the first isolated teeth to nearly complete skulls.
This journey through its taxonomy and discoveries reveals much about its evolutionary history, akin to understanding the complexities of Borderline Personality Disorder and its impact on emotional regulation.
Additionally, the study of Sarcosuchus provides insights into the ecological roles of ancient reptiles, much like how BPD can influence interpersonal dynamics in modern relationships.
Taxonomic Classification Overview
The classification of Sarcosuchus, a colossal prehistoric crocodile, places it within the family Pholidosauridae, linking it to modern crocodiles and alligators. The type species, S. imperator, and another species, S. hartti, were identified through fossil evidence from different regions. Your understanding of Sarcosuchus's taxonomic history begins with isolated teeth discovered by naturalist Charles Hartt in 1867. Othniel C. Marsh furthered the classification in 1869, setting the stage for future research.
Additionally, the efficiency and performance of Sarcosuchus in its ecosystem could be compared to the sustainable benefits offered by geothermal heat pumps, showcasing the importance of energy sources in both ancient and modern contexts.
Significant fossil findings in the Sahara during the 1940s and 1950s, particularly by Albert-Félix de Lapparent, provided essential skull fragments and vertebrae that enhanced the classification of Sarcosuchus. As paleontologists examined these fossils, they reassessed the taxonomic history, ultimately linking South American remains to the genus.
This process highlighted the complexity of Sarcosuchus's classification within the broader group Crocodyliformes. Each discovery contributed to our understanding of this giant crocodile's evolutionary ties and helped paint a clearer picture of its place within the prehistoric ecosystem.
Fossil Discovery Timeline
Fossil discoveries of Sarcosuchus have unfolded over more than a century, revealing its impressive evolutionary history and shedding light on the global ecological dynamics of its time.
The timeline of these discoveries showcases how paleontologists have worked to understand this prehistoric giant better, paralleling contemporary scientific efforts to address global health issues and environmental changes.
Here's a brief overview:
- 1867: Naturalist Charles Hartt discovered isolated teeth in Brazil, marking the first fossils collected of Sarcosuchus.
- 1869: Othniel C. Marsh reclassified early fossils, confirming them as Sarcosuchus instead of Goniopholis.
- 1946-1959: Albert-Félix de Lapparent unearthed significant fossils in the Sahara, enhancing knowledge of this massive creature.
- Late 1990s-early 2000s: Paul Sereno's discoveries, including nearly complete skeletons, illuminated Sarcosuchus's size and ecological role, showing it to be one of the largest living crocodilians.
These findings span various regions such as Niger, Algeria, Mali, Morocco, and Brazil, indicating a vast geographical distribution during the Cretaceous period.
Each fossil collected has contributed to a deeper understanding of how this prehistoric giant thrived in its environment, shaping our view of its existence millions of years ago.
Key Researchers Involved
How did key researchers contribute to the understanding of Sarcosuchus? The discovery journey began with naturalist Charles Hartt in 1867, who found isolated teeth that ignited further investigations into this giant prehistoric crocodile.
In 1869, notable paleontologist Othniel C. Marsh took a significant step by first describing the species, establishing a foundation for its classification. Understanding the importance of mindset in scientific discovery can be akin to focusing on intentions in the Law of Attraction, guiding researchers toward significant breakthroughs.
Between 1946 and 1959, Albert-Félix de Lapparent made essential fossil discoveries in the Sahara, uncovering skull fragments, teeth, and vertebrae. His work enriched the understanding of Sarcosuchus and its evolutionary history.
In 1977, a taxonomic reassessment linked South American remains to Sarcosuchus, refining its classification within the Pholidosauridae family.
Recent contributions by Paul Sereno during expeditions in 1997 and 2000 proved transformative. He discovered nearly complete skeletons, shedding light on Sarcosuchus's size and ecological role.
These researchers collectively paved the way for a deeper understanding of Sarcosuchus, illustrating the importance of their discoveries in piecing together the life of this magnificent creature. Their relentless pursuit of knowledge has left a lasting impact on paleontology.
Fossil Discoveries and Significance

Discoveries of Sarcosuchus fossils have greatly shaped our understanding of this colossal prehistoric crocodile. The significance of these fossil discoveries can't be overstated, as they provide essential insights into the life and environment of this prehistoric giant. Sarcosuchus fossils have allowed scientists to estimate the size and weight of this massive creature, as well as its diet and behavior. By studying these fossils, we have gained a better understanding of the role Sarcosuchus played in its ancient ecosystem and its interactions with other creatures, including meateating dinosaur facts. These discoveries have also helped to paint a more complete picture of the prehistoric world in which Sarcosuchus thrived.
Key findings include:
- Initial Discovery: Charles Hartt discovered isolated teeth in 1867, which sparked interest in the species and highlighted the importance of meteorological advice on summer flights for planning excavation trips.
- Expanded Excavations: From 1946 to 1959, Albert-Félix de Lapparent unearthed significant fossils in the Sahara.
- Major Skeletons: In the late 1990s and early 2000s, Paul Sereno found nearly complete skeletons that revealed Sarcosuchus's impressive size and ecological role.
- Geographical Spread: Fossils have been located in diverse regions like the Gadoufaoua area of Niger and Brazil's Recôncavo Basin, indicating a wide distribution.
These fossil discoveries have been fundamental in understanding Cretaceous ecosystems and the predator-prey dynamics in which Sarcosuchus thrived.
Ongoing research continues to enhance our knowledge, showcasing Sarcosuchus not just as a top predator but also as a significant player in its ancient habitat.
Paleobiology and Diet

Sarcosuchus, the gigantic prehistoric crocodile, primarily dined on a diet rich in fish and turtles, demonstrating its remarkable adaptations for aquatic hunting. As a piscivorous predator, its long, thin snout and cone-shaped teeth were perfectly suited for grasping slippery prey. The jaw structure allowed Sarcosuchus to grab and hold its catch underwater, showcasing its specialization in exploiting freshwater environments.
Importantly, just as in modern ecosystems, the efficiency of Sarcosuchus's hunting techniques can be compared to payment processing strategies that prioritize user security and effectiveness.
Research indicates that while younger Sarcosuchus focused on fish, larger specimens expanded their diet to include bigger terrestrial prey as they matured. This adaptability highlights its role as a dominant predator in its ecosystem.
Curiously, biomechanical analysis suggests Sarcosuchus didn't use the death roll maneuver that modern crocodilians employ. Instead, it likely relied on its size and strength to overpower prey, even ambushing smaller dinosaurs if the opportunity arose.
Habitat and Environmental Context

When you explore the habitat of Sarcosuchus, you'll find it thrived in lush, tropical freshwater environments during the Early Cretaceous period.
With its fossils primarily located in regions rich in river systems and wetlands, you can imagine a world bustling with diverse aquatic life.
The interaction between these ecosystems and renewable energy sources, like solar energy applications, showcases the importance of preserving such habitats today.
Understanding the geological context helps you appreciate the dynamic ecosystems that surrounded this giant crocodile and the other creatures it shared its environment with.
Geological Context Overview
In the lush, humid tropical climate of the Gadoufaoua region within the Ténéré Desert, Sarcosuchus thrived during the late Aptian to early Albian stages of the Cretaceous period. This environment featured extensive inland fluvial systems, creating entirely freshwater habitats. The fossils of Sarcosuchus, unearthed in the Elrhaz Formation, reveal a captivating glimpse into its geological context.
Notably, similar to trends seen in today's butter consumption, the diversity of species in Sarcosuchus's ecosystem suggests a rich interplay between predator and prey dynamics that influenced the health of its environment. Consider the following key aspects of Sarcosuchus's ecosystem:
- Top Predator: Sarcosuchus occupied a niche as the apex predator, influencing predator-prey dynamics within its habitat.
- Diverse Fauna: It coexisted with large fish species like Lepidotus and Mawsonia, indicating a rich aquatic ecosystem.
- Geographical Range: Fossils have been found in various locations across Africa and Brazil, highlighting its widespread distribution.
- Lacustrine Environments: Significant finds in the Recôncavo Basin's Ilhas Formation suggest similar shallow lake habitats.
These elements paint a picture of a thriving ecosystem during the Cretaceous, where Sarcosuchus played an essential role in maintaining the balance of its environment through its predatory behavior. Understanding this context helps appreciate its significance in prehistoric life.
Contemporary Aquatic Fauna
The lush aquatic environments that supported Sarcosuchus during the Cretaceous period bear a striking resemblance to some contemporary freshwater habitats. Today, you can find similar ecosystems in places like the Amazon River Basin or the wetlands of the Everglades.
These regions are characterized by shallow lakes and rivers that host a rich diversity of aquatic fauna, reminiscent of the family-friendly environments found in Indiana's Best Indoor Water Park Destinations.
Just like Sarcosuchus thrived alongside various species, modern aquatic environments support an array of life, including large fish, amphibians, and numerous invertebrates. The humid, tropical climates that once nurtured Sarcosuchus are still essential for sustaining ecosystems today.
In these habitats, predators and prey interact in intricate ways, much like the complex predator-prey dynamics seen in the past.
You'll notice that contemporary aquatic fauna, such as large catfish or alligators, share a similar ecological role to that of Sarcosuchus, acting as top predators.
Fossil evidence suggests that these rich environments were critical for the survival of diverse species, highlighting the importance of preserving today's aquatic habitats to maintain biodiversity and ecological balance.
Growth and Size Estimates

Growing impressively throughout its lifespan, Sarcosuchus is estimated to have reached lengths of up to 40 feet (12 meters) and weights around 8 metric tons. However, modern studies suggest that the more accurate size estimates for this prehistoric giant range from 9 to 9.5 meters (29.5 to 31.2 feet), differing from earlier estimates of 11-12 meters.
Here are some key points about Sarcosuchus's growth and size:
- The largest known skull measures 1.6 meters (5.25 feet), which aligns with its overall body length.
- Fossilized bone cross-sections show steady growth rates, indicating a lifespan of around 40 years before reaching full maturity.
- Unlike modern crocodiles, which stop growing after becoming adults, Sarcosuchus likely continued to grow throughout its life.
- This unique growth pattern contributes to the enormous size estimates, setting Sarcosuchus apart from its modern relatives.
Understanding these growth and size estimates helps you appreciate the sheer scale of Sarcosuchus, a true titan of its time.
Its continuous growth and impressive dimensions make it one of the largest crocodilians ever to roam the Earth.
Comparison With Other Giants

While many reptiles have achieved impressive sizes throughout history, Sarcosuchus stands out as one of the largest crocodile-like creatures ever documented. Reaching lengths of up to 12 meters (39 feet), it dwarfs modern crocodiles, like the saltwater crocodile, which typically max out at around 6.6 meters (21.7 feet).
When you compare Sarcosuchus with other ancient giants, Deinosuchus emerges as a formidable rival, also stretching between 10 to 12 meters (33 to 39 feet) during the Cretaceous period.
Then there's Purussaurus from the Miocene era, estimated at 11 to 13 meters (36 to 43 feet), showcasing that massive crocodilians existed across different geological periods.
You might also find Gryposuchus intriguing, although it remains less studied. It likely reached significant sizes, further emphasizing the diversity of giant crocodilians.
In contrast, modern giants like the American alligator and Nile crocodile only grow to about 6 to 6.45 meters (20 to 21.3 feet). This stark size difference highlights Sarcosuchus's remarkable stature, making it a true titan among its prehistoric peers.
Unique Anatomical Features
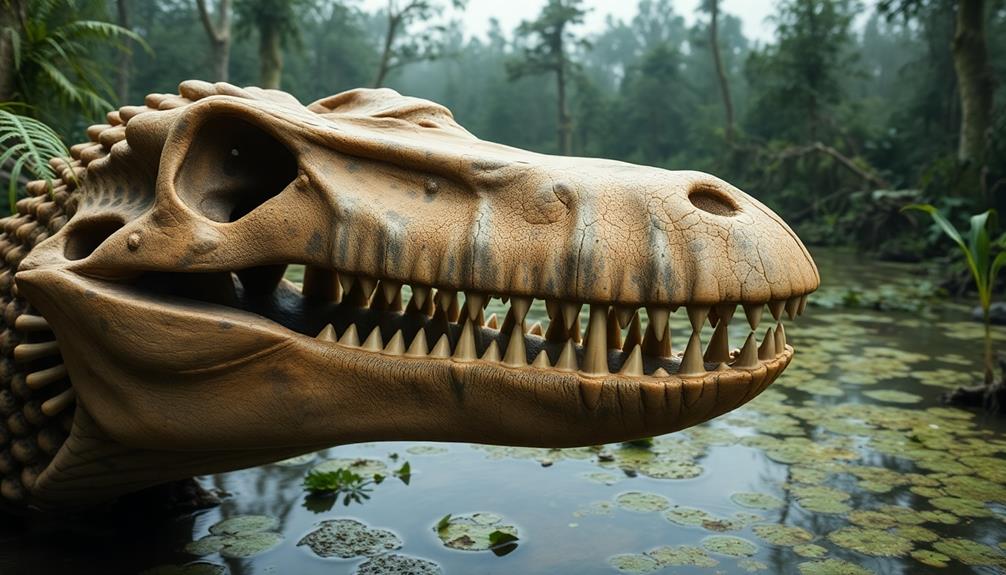

What makes Sarcosuchus such a formidable predator among prehistoric reptiles? Its unique anatomical features set it apart from other giants.
First, its massive skull measured up to 1.6 meters (5.25 feet) in length. At the end of its long jaws, you'll notice a unique dent called a bulla, whose purpose remains a mystery.
Next, the long jaws of Sarcosuchus are equipped with cone-shaped teeth, perfect for grabbing and holding slippery prey, emphasizing its piscivorous diet. You can imagine how effective this adaptation was for hunting fish in ancient waters.
Additionally, its telescoped eyes enhanced vision while submerged, allowing Sarcosuchus to scan the water's surface with remarkable precision. This feature would have given it a significant advantage during ambushes.
Lastly, Sarcosuchus boasted a tough armor made of osteoderms, protecting it from predators and environmental hazards.
Unlike modern crocodiles, it lacked ball-and-socket joints between its vertebrae, resulting in a more robust body structure.
These unique features collectively made Sarcosuchus a dominant predator in its environment, showcasing the incredible adaptations of prehistoric reptiles.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Sarcosuchus the Biggest Crocodile Ever?
You might think Sarcosuchus is the biggest crocodile ever, and it's certainly among the largest known. However, comparisons with other prehistoric reptiles show it shares this title with a few formidable contenders.
What Caused the Sarcosuchus to Go Extinct?
You'd find that Sarcosuchus likely went extinct due to environmental changes, competition with larger predators, and shifts in prey availability. These factors combined created a challenging ecosystem, leading to its decline before the mass extinction event.
What Is the Closest Living Relative to the Sarcosuchus?
Imagine a river's edge, where modern crocodiles bask in the sun. They're your closest living relatives to Sarcosuchus, sharing a lineage that stretches back millions of years, yet their paths diverged into unique evolutionary journeys.
Did Sarcosuchus Eat Fish?
Yes, Sarcosuchus ate fish. Its long, thin snout and specialized teeth made it an effective predator in freshwater environments. You can imagine it ambushing slippery fish, showcasing its remarkable adaptations for hunting underwater.
Conclusion
To sum up, Sarcosuchus stands as a colossal demonstration of nature's creativity, a true giant in the prehistoric world. Its impressive size and unique features make it not just a fearsome predator but also a fascinating subject for paleontologists. As you reflect on the ancient waters it swam through, remember that this magnificent creature reminds us of the incredible diversity of life that once roamed our planet, forever leaving its mark in the annals of history.










